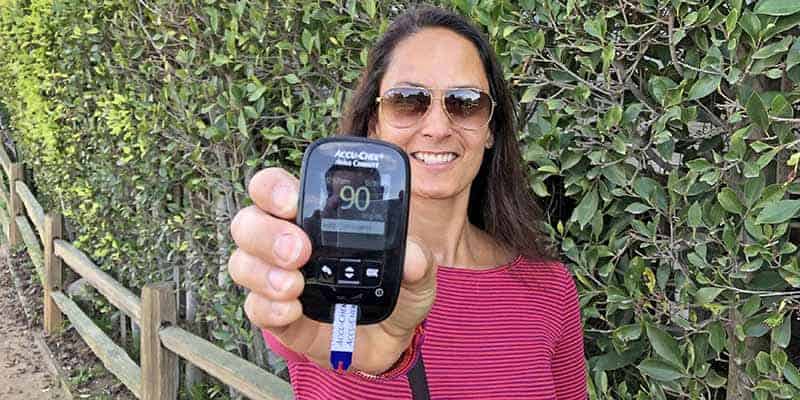
Your blood glucose (sugar) ranges are a vital a part of your general well being and your physique’s means to operate correctly.
For these of us with diabetes, striving to attain “regular” blood sugar ranges is a continuing, hour-by-hour pursuit. And it isn’t simple.
On this article, we’ll take a look at regular blood sugar ranges and purpose ranges for individuals with out diabetes and advisable blood sugar targets for individuals with prediabetes, sort 1 diabetes, and sort 2 diabetes.
Regular blood sugar ranges in individuals with out diabetes (chart)
For an individual with none sort of diabetes, blood sugar ranges are typically between 70 to 99 mg/dL (3.9 to five.5 mmol/L) fasting and underneath 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) after a meal.
Listed here are the traditional blood sugar ranges for an individual with out diabetes based on the NIH:
| Fasting Blood Sugar (e.g., Within the Morning Earlier than Consuming) | Lower than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) |
| 1 to 2 Hours After a Meal | Lower than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) |
| 2 to three Hours After a Meal | Lower than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) |
Really useful blood sugar ranges in individuals with diabetes (chart)
Listed here are the commonly advisable blood sugar ranges for an individual with diabetes based on the ADA:
| Fasting Blood Sugar (e.g., Within the Morning Earlier than Consuming) | 80 to 130 mg/dL (4.4 to 7.2 mmol/L) |
| 1 to 2 Hours After a Meal | Lower than 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L) |
Study extra about fasting and after-meal blood sugar ranges in: Blood Sugar Chart: Blood Sugar and A1c Targets.
How have you learnt what your blood glucose stage is?
Except it’s pretty excessive or low, you typically can’t really feel what your blood sugar stage is. And in reality, chances are you’ll not even have the ability to inform from bodily signs when it’s excessive or low.
The easiest way to know your blood sugar stage is to both examine it with a conventional glucose meter or use a CGM (steady glucose monitor) machine.
For a glucose meter, you do a finger-stick with a lancet, put a drop of blood onto a take a look at strip, after which insert the strip into the meter for a studying. With a CGM, readings are taken from the interstitial fluid (the fluid between the cells) about each 5 minutes by way of a sensor inserted slightly below the pores and skin.
Diagnosing prediabetes, sort 1, and sort 2 diabetes
The next are assessments which may be utilized by your healthcare supplier to find out when you’ve got diabetes:
Checks used to diagnose diabetes
Fasting plasma glucose take a look at
This take a look at measures your glucose stage at a single time limit, sometimes after you’ve got been fasting (nothing to eat or drink besides water) for a minimum of 8 hours.
Random glucose take a look at
This take a look at measures your glucose stage at a single time limit and could also be given at any time, whether or not you’ve got fasted or not.
Oral glucose tolerance take a look at (OGTT)
For this take a look at, you’ll have a blood pattern taken after fasting for a minimum of 8 hours. Subsequent, you’ll drink a liquid excessive in sugar and could have one other blood pattern taken after 2 hours to see how your blood glucose ranges have modified.
(In those that are pregnant, glucose will probably be checked each hour for two to three hours to check for gestational diabetes.)
A1c take a look at
This blood take a look at displays your common glucose ranges over the earlier 2 to three months. You possibly can eat and drink previous to having an A1c take a look at.
A repeat of those assessments is usually required to substantiate a diabetes prognosis.
Check outcomes for diagnosing diabetes (chart)
The next blood sugar and A1c outcomes (a measure of glucose management over the earlier 2 to three months) are used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes, based on the ADA:
| A1c | Fasting Glucose | 2 Hours After a Meal | |
| Prediabetes | 5.7 to six.4 % | 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to six.9 mmol/L) | 140 mg/dL to 199 mg to dL (7.8 to 11.1 mmol/L) |
| Diabetes (sort 1 or sort 2) | 6.5 % or greater | 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or greater | 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or greater |
Study extra about diagnosing diabetes in: Sorts of Diabetes.
Please observe: Kind 1 diabetes tends to develop in a short time, which implies that by the point signs are felt, blood sugar ranges are sometimes effectively above 200 mg/dL on a regular basis. For many individuals, signs come on so rapidly that they’re dismissed as a lingering flu or one other seemingly strange virus.
By the point blood sugar ranges are checked, many individuals with undiagnosed sort 1 diabetes could have ranges above 400 mg/dL or greater.
In the event you suspect that you just or a liked one has sort 1 diabetes, go to your main care or pressing care instantly and ask for a urine take a look at to measure ketones along with checking blood sugar ranges and A1c.
Learn extra about ketones at prognosis in: Tips on how to Keep away from Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA).
Your A1c and blood sugar targets
Managing any sort of diabetes is way extra sophisticated than giving an individual some insulin and telling them to maintain their blood sugars inside X and X mg/dL. In the event you’ve lived with diabetes for quite a lot of days, you most likely already know this.
What’s A1c?
“A1c, also referred to as hemoglobin A1c, HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin, or glycohemoglobin, is a blood take a look at that measures your common blood sugar over the past 2 to three months,” explains Christel Oerum, MS, in Diabetes Robust’s information to reducing your A1c.
Though the take a look at displays the glucose hooked up to hemoglobin (the protein in your pink blood cells) over the previous 2 to three months, the blood sugar ranges within the 2 weeks main as much as your A1c take a look at affect the outcomes probably the most. Primarily, greater blood sugar ranges throughout this era lead to extra glucose binding to hemoglobin.
Translating your A1c to a blood sugar stage
Utilizing this straightforward calculator from the ADA, you possibly can translate your most up-to-date A1c end result to an “eAG,” or “estimated common glucose stage.”
You can too use this translation when working to enhance your A1c and obtain nearer to regular blood sugar ranges.
As an example, if an A1c of 6.0 % equates to a median blood sugar stage of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L), then you possibly can take a look at your present blood sugar outcomes in your CGM and meter and pinpoint what time of day you’re ceaselessly greater than that stage.
| A1c | eAG |
| 6 % | 126 mg/dL |
| 7 % | 154 mg/dL |
| 8 % | 183 mg/dL |
| 9 % | 212 mg/dL |
| 10 % | 240 mg/dL |
| 11 % | 269 mg/dL |
| 12 % | 298 mg/dL |
Regular blood sugar ranges in an individual with out diabetes can lead to an A1c of 5.6 % or decrease.
Only a decade or two in the past, it was uncommon for an individual with sort 1 diabetes to attain an A1c end result under 6.0 %.
Due to new and improved insulin and higher expertise like CGMs, smarter insulin pumps, and hybrid closed-loop expertise (which permits some insulin doses to be mechanically delivered), extra individuals with diabetes at the moment are in a position to safely obtain A1c ranges within the greater 5 % vary.
Why your A1c issues
In a nutshell: Your A1c is without doubt one of the clearest indicators of your danger for growing diabetes problems like neuropathy (nerve injury), retinopathy (a kind of eye illness), nephropathy (kidney illness), heart problems, and extreme an infection in any a part of your physique that requires therapeutic.
As an example, a small reduce in your toe may grow to be contaminated resulting from excessive blood sugars, wrestle to heal, and grow to be extreme sufficient that the an infection may require an amputation.
The final tips from the ADA suggest an A1c stage of lower than 7.0 % to assist forestall diabetes-related problems. Reducing your A1c nearer to six.0 % could additional scale back the chance of microvascular problems (these impacting the small blood vessels), comparable to these affecting the eyes (retinopathy), kidneys (nephropathy), and nerves (neuropathy).
Some individuals with diabetes goal for A1c ranges within the 5s and decrease — particularly those that observe strict low-carb diets just like the ketogenic food plan and the Bernstein food plan. Nevertheless, this hasn’t been confirmed in analysis as particularly vital, neither is it moderately achievable for the bigger inhabitants of individuals with diabetes.
It’s additionally necessary to keep in mind that your blood sugar ranges and your A1c are simply data that tells you whether or not your physique wants adjustments in components like insulin, different diabetes drugs like metformin, your vitamin, or your bodily exercise.
In the event you don’t just like the quantity you’re seeing in your glucose meter or your A1c outcomes, use that quantity as motivation to make adjustments (with the assist of your diabetes healthcare staff) in the way you safely handle your diabetes with the intention to get completely different outcomes.
Figuring out the precise A1c purpose for you
Simply because a blood sugar vary of 70 to 130 mg/dL (3.9 to 7.2 mmol/L) is taken into account the healthiest for individuals with diabetes doesn’t essentially imply that’s the suitable purpose vary for you — particularly when you’ve got sort 1 diabetes, or take insulin as an individual with sort 2 diabetes.
The explanation this will not be the precise purpose for you is that extraordinarily tight blood sugar administration in individuals taking insulin can probably result in frequent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), which may be harmful.
Reaching extraordinarily tight blood sugar administration additionally typically requires a strict vitamin plan, very frequent blood sugar monitoring, exact remedy administration, and, typically, years of expertise learning your blood sugar ranges.
Your A1c targets must be set in shut session together with your medical staff, who might help steadiness the advantages and dangers of various targets primarily based in your well being standing, life-style, and preferences.
Older adults with cognitive or useful limitations or extreme comorbidities (main further well being points) could have a less-stringent A1c purpose of lower than 8 %.
Additionally it is value noting that your A1c targets can change over time as your diabetes administration evolves.
A1c targets must be individualized
“A1c targets must be individualized primarily based on the person capabilities, dangers, and prior experiences,” explains Gary Scheiner, MS, CDCES, founding father of Built-in Diabetes and creator of “Suppose Like a Pancreas“.
“For instance, we typically goal for very tight A1c ranges throughout being pregnant and extra conservative targets in younger youngsters and the aged.”
Scheiner highlights necessary components that might justify aiming for the next A1c, like hypoglycemia unawareness, a situation during which an individual with diabetes not feels the everyday warning indicators of low blood sugar.
Hypoglycemia unawareness can put you at vital danger for extreme low blood sugars which have the potential to be life-threatening. To scale back that danger, you’ll goal for greater goal blood sugar ranges.
“Somebody with vital hypoglycemia unawareness and a historical past of extreme lows ought to goal greater blood glucose ranges than somebody who can detect and handle their lows extra successfully,” provides Scheiner.
“And definitely, somebody who has been working A1cs in double digits [like 10 percent or higher] for fairly a while shouldn’t be focusing on an A1c of 6 % … higher to set modest, reasonable, achievable targets.”
Examine decreasing your A1c in: Tips on how to Decrease Your A1c and Tips on how to Decrease A1c Naturally.
Your blood sugar isn’t simply due to what you eat
It’s simple to consider that your blood sugar ranges are impacted solely by what you eat and the way a lot you train, however individuals with sort 1 and sort 2 diabetes who examine their blood sugars ceaselessly may let you know in any other case.
It’s particularly necessary to maintain this in thoughts when taking a look at your personal blood sugars and your targets, as a result of there are specific variables and challenges that affect blood sugar ranges which you can’t at all times management.
For instance:
- Menstrual cycles: typically increase blood sugar and insulin wants
- Adrenaline rushes from aggressive sports activities, heated arguments, curler coaster rides, and different intense conditions: increase blood sugar and insulin wants
- The widespread chilly and different sicknesses: normally increase blood sugar and insulin wants
- Hormonal adjustments resulting from puberty and wholesome progress in younger adults: increase blood sugar and insulin wants
- An damage that will increase general irritation ranges: raises blood sugar and insulin wants
- Gluconeogenesis throughout anaerobic train: raises blood sugar and insulin wants
When you can’t essentially forestall these components that have an effect on your blood sugar from occurring, you possibly can work together with your diabetes healthcare staff to regulate your insulin, different diabetes drugs, vitamin, and exercise ranges to assist compensate for them after they do happen.
For instance, when participating in anaerobic train comparable to weightlifting, many individuals with sort 1 diabetes discover it essential to take a small bolus of insulin previous to or throughout their exercise as a result of anaerobic train can truly increase blood sugar.
Remaining ideas: Nonetheless pissed off together with your blood sugar and A1c outcomes?
Your blood sugars and your insulin or remedy wants by no means keep in a single place. In the event you acquire weight or drop pounds, your insulin and drugs wants will change. In the event you grow to be extra lively or much less lively, your wants will change. In the event you make drastic and even small adjustments to your vitamin, your wants will change.
Working together with your diabetes healthcare staff and diabetes coaches who can educate you tips on how to make adjustments in your general diabetes administration plan is crucial. Diabetes is a lifelong studying course of.
Take a deep breath and be affected person. In the event you don’t like what you’re seeing in your glucose meter, don’t get mad … get learning! Take good notes and work together with your staff to make adjustments to succeed in your targets.